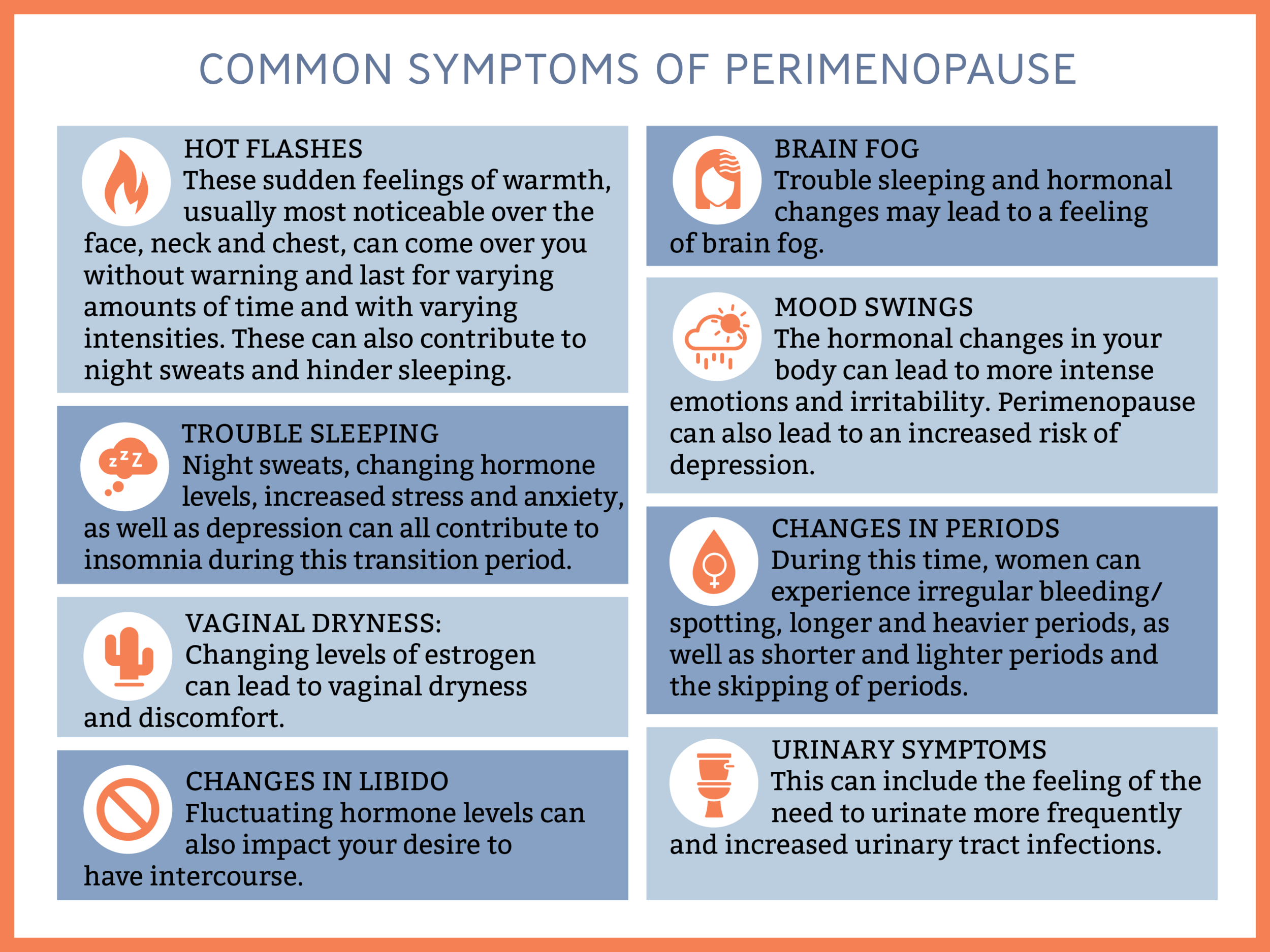
As we traverse the journey of life, women encounter a pivotal transition known as menopause. Preceding this milestone is a phase called perimenopause, marked by a myriad of physical, emotional, and reproductive changes. Embarking on an exploration of these signs and symptoms, we aim to shed light on this transformative experience, empowering women with knowledge and support.
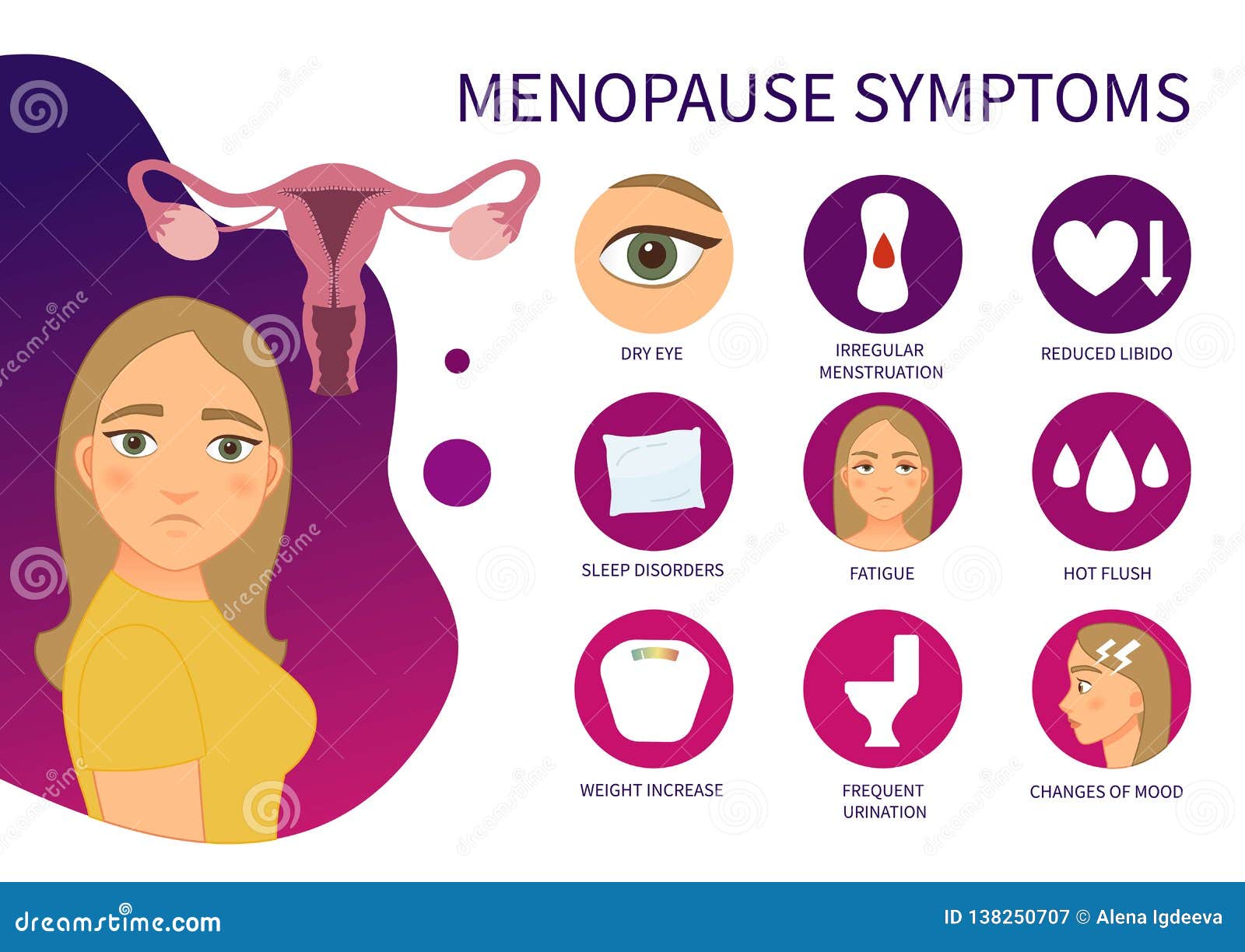
From the telltale hot flashes to the emotional roller coaster, perimenopause and menopause can present a unique set of challenges. Understanding these manifestations is crucial for navigating this phase with grace and resilience.
Emotional Symptoms of Perimenopause
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2322667-article-early-signs-of-menopause-5a4cfd9af1300a00373f55f9.png)
Perimenopause, the transitional phase leading up to menopause, often brings about a rollercoaster of emotions. Mood swings, irritability, and anxiety are common experiences during this time.
Mood Swings
The hormonal fluctuations of perimenopause can trigger unpredictable shifts in mood. You may feel elated one moment and irritable the next. These mood swings can be challenging to manage and can affect relationships and daily life.
Irritability and Anxiety
Irritability and anxiety are also prevalent emotional symptoms of perimenopause. You may find yourself more easily agitated or overwhelmed by everyday situations. Anxiety can manifest as racing thoughts, difficulty concentrating, and physical symptoms like muscle tension or rapid heartbeat.
Depression and Loss of Interest
Some women experience feelings of depression during perimenopause. This may be due to hormonal changes or other factors such as sleep disturbances or changes in life circumstances. Loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyable is another common symptom.
Cognitive Changes and Memory Lapses
Perimenopause can also affect cognitive function. You may experience difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, or brain fog. These changes can be frustrating and interfere with daily tasks and decision-making.
Irregular Menstrual Patterns
As estrogen levels decline during perimenopause, ovulation becomes increasingly erratic. This leads to changes in the menstrual cycle, including:
Changes in Cycle Length
- The menstrual cycle may become shorter or longer than usual.
- The time between periods may vary significantly.
Changes in Flow
- The menstrual flow may become heavier or lighter than usual.
- Spotting or bleeding between periods may occur.
Cessation of Menstruation (Menopause)
Eventually, as estrogen levels fall below a critical threshold, ovulation ceases altogether. This marks the onset of menopause, which is defined as the absence of menstruation for 12 consecutive months.
Long-Term Health Implications
Perimenopause and menopause can have long-term implications for women’s health. Understanding these risks is crucial for proactive management and preventive measures.
Osteoporosis and Cardiovascular Disease
During menopause, the decline in estrogen levels weakens bones, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. This condition makes bones fragile and prone to fractures, especially in the spine, hips, and wrists.
Menopause also increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Estrogen has protective effects on blood vessels, but its decline can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Weight Gain and Metabolic Changes
Many women experience weight gain during menopause. Hormonal changes can alter metabolism, making it more challenging to maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, the loss of muscle mass that often accompanies menopause can contribute to weight gain.
Metabolic changes during menopause can also affect cholesterol levels and blood sugar regulation. Regular screenings and lifestyle modifications are essential to manage these risks.
Regular Screenings and Preventive Measures
Regular health screenings are crucial for detecting and managing long-term health risks associated with menopause. These screenings may include bone density tests, mammograms, and cholesterol checks.
Preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and adopting a balanced diet can help mitigate the risks of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and weight gain. Lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can help women navigate the challenges of menopause and maintain optimal health.
Management and Treatment Options
Menopause and perimenopause can present with a wide range of symptoms that can impact an individual’s physical and emotional well-being. Management and treatment options aim to alleviate these symptoms and improve overall quality of life during this transition.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT involves administering synthetic or bioidentical hormones to replace the declining levels of estrogen and progesterone during menopause. It can be prescribed in various forms, including pills, patches, or creams.
Benefits of HRT:
- Reduces hot flashes and night sweats
- Improves sleep quality
- Prevents bone loss and osteoporosis
- Alleviates vaginal dryness
Risks of HRT:
- Increased risk of blood clots
- Breast cancer risk (in certain cases)
- Gallbladder disease
- Stroke (in certain cases)
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthy lifestyle modifications can help manage menopausal symptoms and improve overall well-being. These include:
Exercise:
Regular physical activity can reduce hot flashes, improve sleep, and strengthen bones.
Diet:
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage weight gain and improve overall health.
Stress Management:
Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can trigger hot flashes.
Alternative Therapies and Complementary Medicine
Some alternative therapies and complementary medicine approaches may offer additional support in managing menopausal symptoms. These include:
Acupuncture:
Acupuncture may help reduce hot flashes and night sweats.
Herbal Remedies:
Certain herbs, such as black cohosh and red clover, have been traditionally used to alleviate menopausal symptoms. However, their effectiveness and safety require further research.
Mind-Body Therapies:
Techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) can help manage emotional symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Impact on Quality of Life
Perimenopause can significantly impact women’s quality of life. The physical and emotional changes experienced can lead to challenges and adjustments.
Women may experience a range of symptoms, including hot flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbances, mood swings, and vaginal dryness. These symptoms can affect their daily activities, work performance, and relationships.
Coping with Changes
- Seeking support and understanding from family and friends can be invaluable.
- Joining support groups or connecting with other women going through perimenopause can provide a sense of community and validation.
- Lifestyle adjustments, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress-reducing activities, can help manage symptoms.
- Considering hormone therapy or other medical interventions may be necessary to alleviate severe symptoms.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the most common physical symptom of perimenopause?
Hot flashes are the most commonly reported physical symptom of perimenopause.
How does perimenopause affect mood?
Perimenopause can trigger mood swings, irritability, and anxiety due to hormonal fluctuations.
What is the primary cause of irregular menstrual patterns during perimenopause?
The gradual decline in estrogen production disrupts ovulation, leading to irregular menstrual cycles.
Is hormone replacement therapy the only treatment option for menopause symptoms?
No, there are various non-hormonal treatments available, including lifestyle modifications, alternative therapies, and complementary medicine.